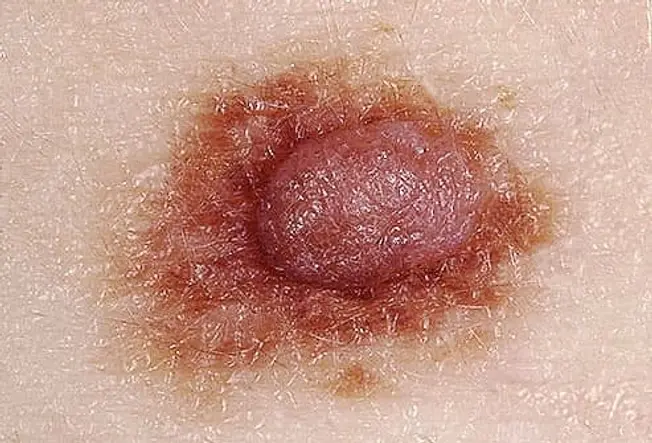
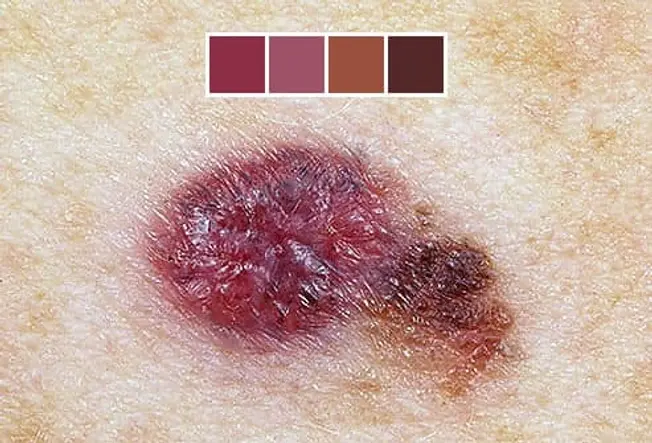
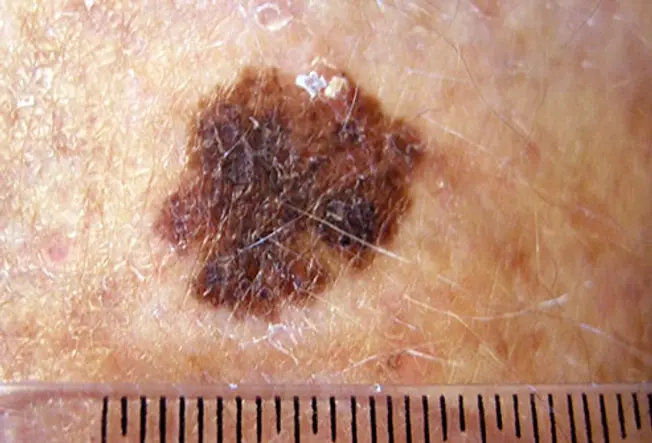
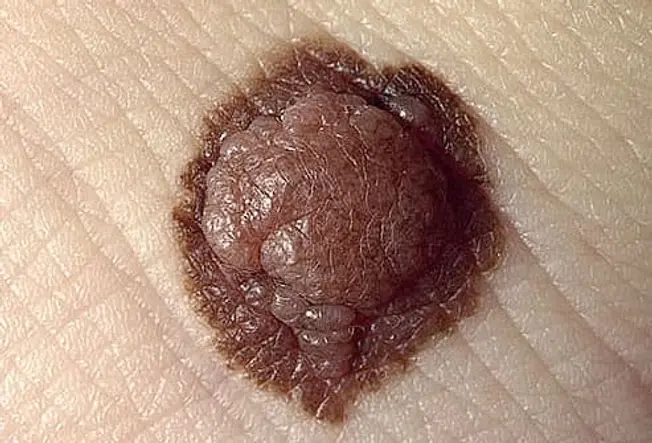
Detecting Skin Cancer Early.
Skin cancers--including melanoma, basal cell carcinoma, and squamous cell carcinoma--often start as changes to your skin. They can be new growths or precancerous lesions--changes that are not cancer but could become cancer overtime. An estimated 40% to 50% of fair-skinned people who live to be 65 will develop at least one skin cancer. Learn to spot the early warning signs.
Skin cancer can be cured if it if found and treated early.
Skin cancer can be cured if it if found and treated early.
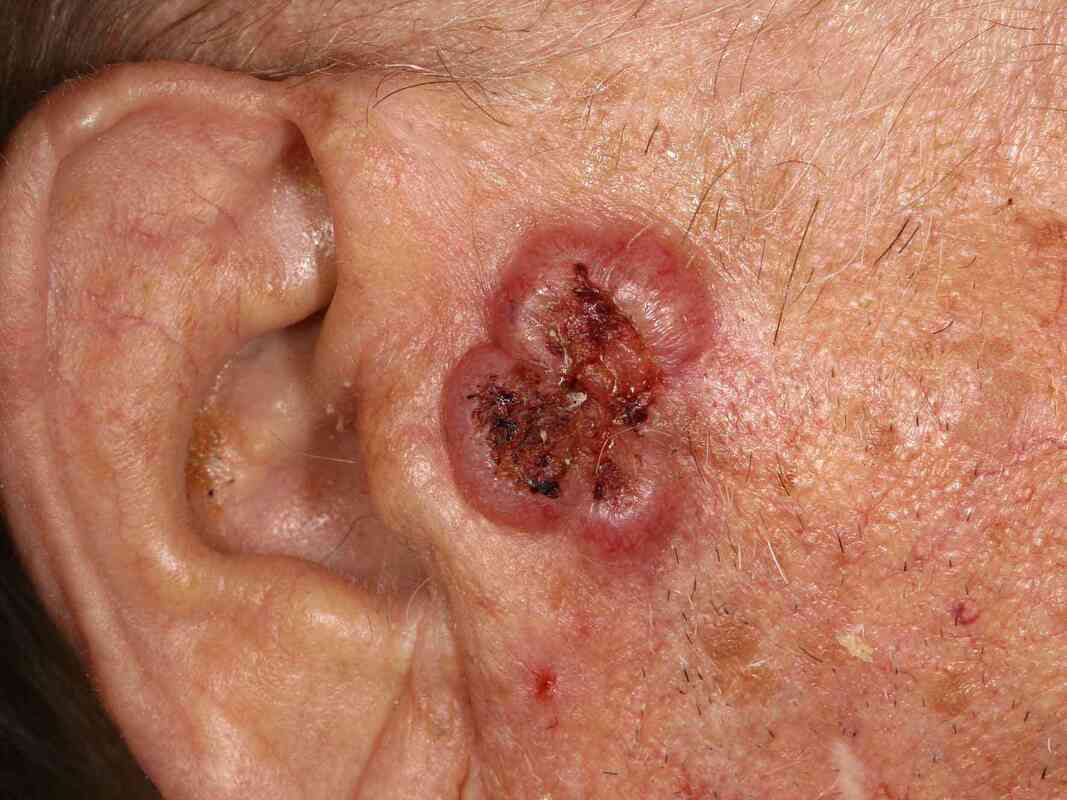
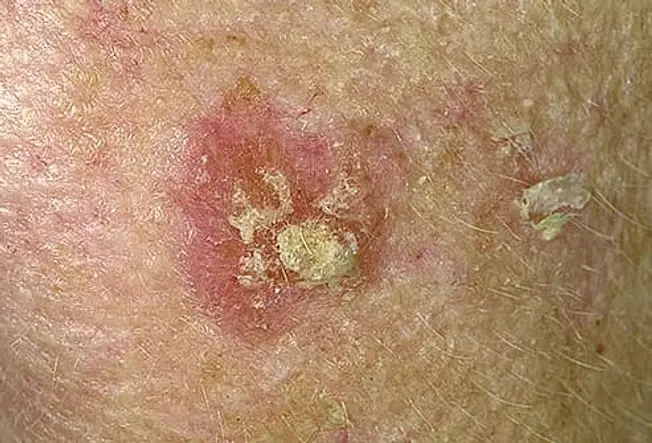
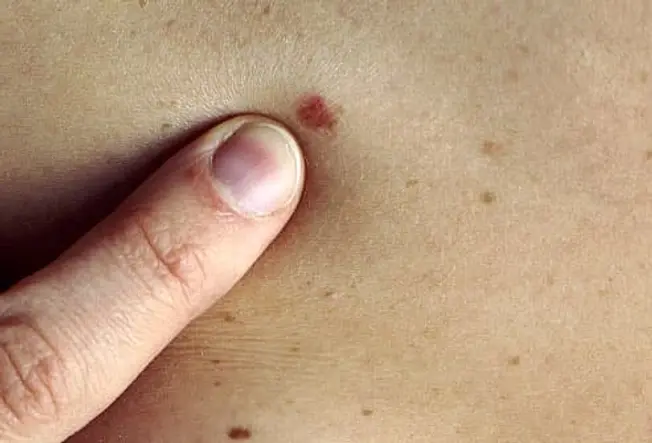
Actinic Keratosis (Solar Keratosis)
These small, scaly patches are caused by too much sun, and commonly occur on the head, neck, and hands, but can be found elsewhere. They can be an early warning sign of skin cancer, but it's hard to tell whether a particular patch will continue to change overtime and become cancerous. Most do not, but doctors recommend early treatment to prevent the early development of squamous cell skin cancer. Fair skinned, blond, or red-- haired people, with blue or green eyes are more at risk.
These small, scaly patches are caused by too much sun, and commonly occur on the head, neck, and hands, but can be found elsewhere. They can be an early warning sign of skin cancer, but it's hard to tell whether a particular patch will continue to change overtime and become cancerous. Most do not, but doctors recommend early treatment to prevent the early development of squamous cell skin cancer. Fair skinned, blond, or red-- haired people, with blue or green eyes are more at risk.
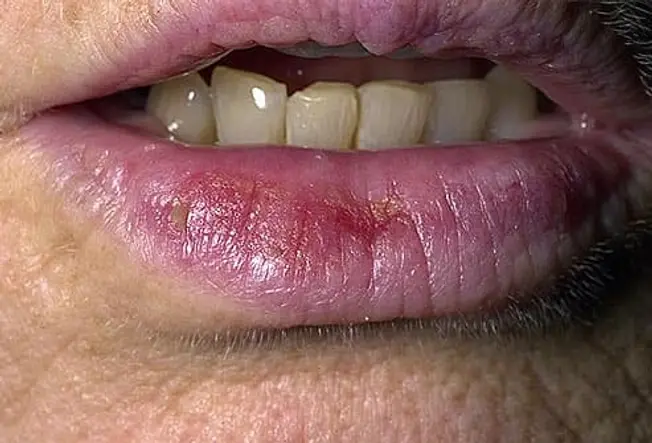
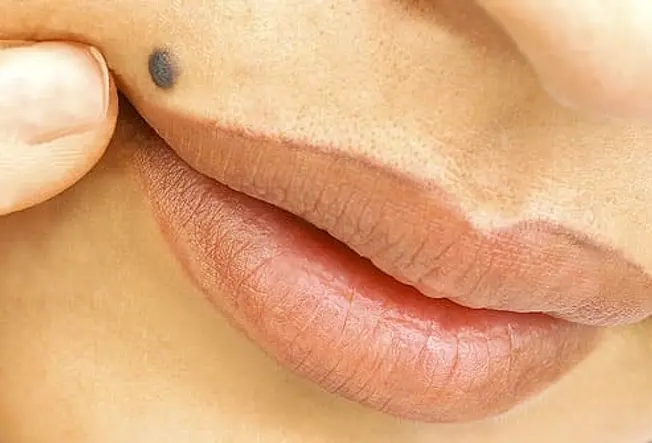
Actinic Cheilitis (Farmer's Lip)
Related to actinic keratosis, actinic cheilitis is a precancerous condition that usually appear on the lower lips. Scaly patches or persistent rough patches on the lips may be present. Less common symptoms include swelling of the lips, loss of the sharp border between the lip and skin, and prominent lip lines.
Actinic cheilitis may evolve into evasive cell squamous carcinoma, if not treated.
Related to actinic keratosis, actinic cheilitis is a precancerous condition that usually appear on the lower lips. Scaly patches or persistent rough patches on the lips may be present. Less common symptoms include swelling of the lips, loss of the sharp border between the lip and skin, and prominent lip lines.
Actinic cheilitis may evolve into evasive cell squamous carcinoma, if not treated.
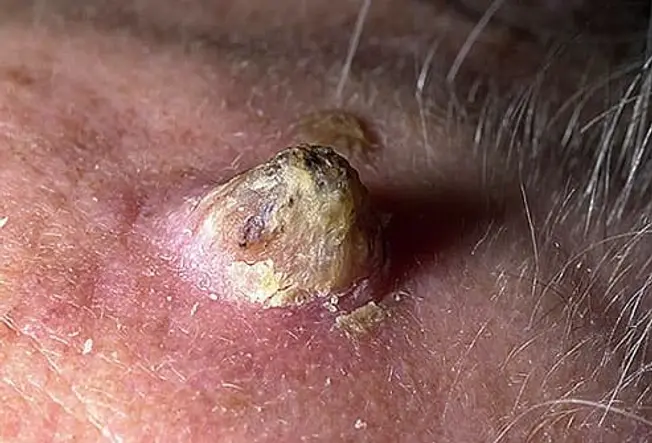
Cutaneous Horns
The cutaneous horn appear as a funnel--shaped growth that extends from the base of the skin. It is composed of compacted keratin ( the same protein in nails). It is a specialized type of actinic keratosis. The size and shape of the growth can vary considerably, but most are a few millimeters in length. Squamous cell carcinoma can be found at the base.It usually appear in fair-skinned elderly adults with a history of significant sun exposure.
The cutaneous horn appear as a funnel--shaped growth that extends from the base of the skin. It is composed of compacted keratin ( the same protein in nails). It is a specialized type of actinic keratosis. The size and shape of the growth can vary considerably, but most are a few millimeters in length. Squamous cell carcinoma can be found at the base.It usually appear in fair-skinned elderly adults with a history of significant sun exposure.
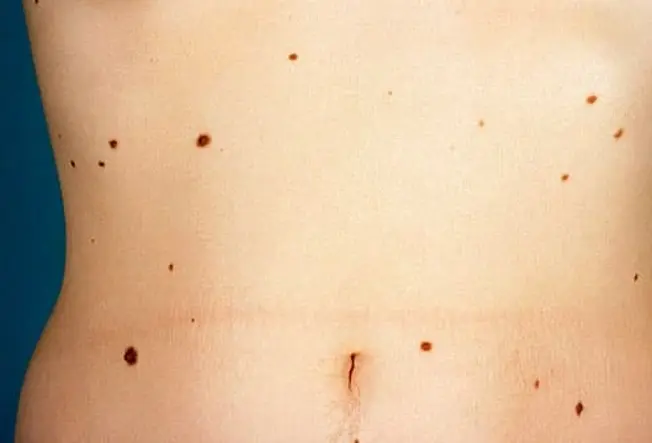
When A Mole Is A Problem
A mole (nevus) is a benign growth of melanocytes, cells that give skin its color. Although few moles become cancer, abnormal or atypical moles can develop into melanoma over time. "Normal" moles can appear flat or raised or may begin flat and become raised overtime. The surface is typically smooth. Moles that may have changed into skin cancer, are often irregularly shaped , contain many colors, and are larger than the size of a pencil eraser.
Most moles develop in youth or young adulthood. It is unusual to acquire a mole in the adult years.
A mole (nevus) is a benign growth of melanocytes, cells that give skin its color. Although few moles become cancer, abnormal or atypical moles can develop into melanoma over time. "Normal" moles can appear flat or raised or may begin flat and become raised overtime. The surface is typically smooth. Moles that may have changed into skin cancer, are often irregularly shaped , contain many colors, and are larger than the size of a pencil eraser.
Most moles develop in youth or young adulthood. It is unusual to acquire a mole in the adult years.
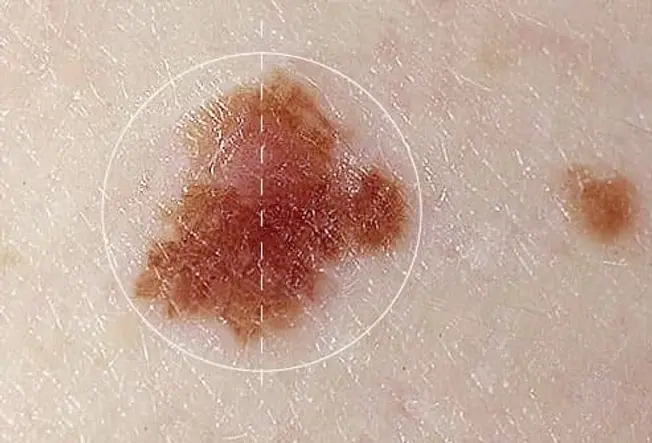
Dysplastic Nevi (Atypical Moles)
Atypical moles are not cancer but can become cancer. They can be found in sun--exposed or sun --protected areas of the body. Atypical moles can be larger( one-quarter inch across or larger) and more irregular in shape, with notched or fading borders. They may be flat or raised or the surface smooth or rough. They are typically of mixed colors, including including pink, red , tan, and brown.
(We'll be back. Stay tuned)
Atypical moles are not cancer but can become cancer. They can be found in sun--exposed or sun --protected areas of the body. Atypical moles can be larger( one-quarter inch across or larger) and more irregular in shape, with notched or fading borders. They may be flat or raised or the surface smooth or rough. They are typically of mixed colors, including including pink, red , tan, and brown.
(We'll be back. Stay tuned)
Know Your ABCDEs
Most moles on a person's body look similar to one another. A mole or freckle that looks different from the others or that has the characteristics of ABCDEs of melanoma should be checked by a dermatologist. It could be cancerous. The ABCDEs are important characteristics to consider when examining your moles or other skin growths.
Most moles on a person's body look similar to one another. A mole or freckle that looks different from the others or that has the characteristics of ABCDEs of melanoma should be checked by a dermatologist. It could be cancerous. The ABCDEs are important characteristics to consider when examining your moles or other skin growths.
Your ABCDEs "A" is for Asymmetry.
Asymmetry means one half of the mole does match the other half. Normal moles are symmetrical. When checking your moles or freckles, draw an imaginary line through the middle and compare the two halves. If they do not look the same on both sides have it checked by a dermatologist.
Asymmetry means one half of the mole does match the other half. Normal moles are symmetrical. When checking your moles or freckles, draw an imaginary line through the middle and compare the two halves. If they do not look the same on both sides have it checked by a dermatologist.
Your ABCDEs. "B" is for Border
If the border of edges of the mole are ragged, blurred, or irregular, have it checked by a dermatologist. Melanoma lesions often have uneven borders.
If the border of edges of the mole are ragged, blurred, or irregular, have it checked by a dermatologist. Melanoma lesions often have uneven borders.
Your ABCDEs "C" is for Color
A mole that does not have the same throughout or that has shades of tan, black, blue, white or red is suspicious. Normal moles are usually a single shade of color. A mole of many shades ot that has darkened or lightened should be checked by a doctor.
A mole that does not have the same throughout or that has shades of tan, black, blue, white or red is suspicious. Normal moles are usually a single shade of color. A mole of many shades ot that has darkened or lightened should be checked by a doctor.
Your ABCDEs "D" is for Diameter.
If you have a mole that appears to be getting larger or is changing color or size or is itching or bleeding, you should consider it suspicious.
If you have a mole that appears to be getting larger or is changing color or size or is itching or bleeding, you should consider it suspicious.
Your ABCDEs "E" is for Evolving.
A mole that is evolving--shrinking, growing larger, changing color, beginning to itch or bleed--should be checked. If a portion of the mole appears newly elevated, or raised from the skin, have it looked at by a doctor. Melanoma lesions often grow in size or change in height rapidly.
A mole that is evolving--shrinking, growing larger, changing color, beginning to itch or bleed--should be checked. If a portion of the mole appears newly elevated, or raised from the skin, have it looked at by a doctor. Melanoma lesions often grow in size or change in height rapidly.
How are Moles Evaluated?
If you find a mole or spot that has any ABCDE's, of melanoma-- or one that's tender, oozing, scaly, doesn't heal or has redness or swelling beyond the mole-- see a doctor. Your doctor may want to remove a tissue sample from the mole and biopsy it. If found to be cancerous, the entire mold and the rim of normal skin around it will be removed and the wound stitched closed.
Additional treatment may be needed.
Credit: WebMD
If you find a mole or spot that has any ABCDE's, of melanoma-- or one that's tender, oozing, scaly, doesn't heal or has redness or swelling beyond the mole-- see a doctor. Your doctor may want to remove a tissue sample from the mole and biopsy it. If found to be cancerous, the entire mold and the rim of normal skin around it will be removed and the wound stitched closed.
Additional treatment may be needed.
Credit: WebMD