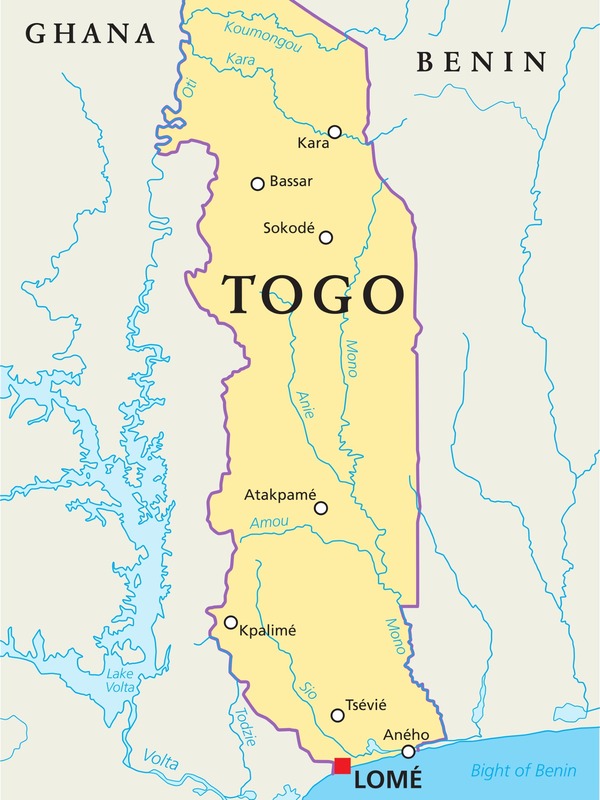
Togo is a country in West Africa. It is bordered by Ghana to the west, Benin to the east, and Burkina Faso to the north. It extends south to the Gulf Guinea where it's capital and largest city, Lome is located. Togo is a small tropical country which covers 22,000 square miles and has a population of approximately 8 million. The width of this country is just 71 miles between Ghana and its eastern neighbor Benin.
Until 1884 what is now Togo was an intermediate zone between the states of Asante and Dahomey, and its various ethnic groups lived in general isolation from each other. In 1884 it became part of Togoland German protectorate, which was later occupied by British and French forces in 1914. In 1922 The League of Nations assigned Togoland to France and the western portion to Britain. In 1946 the British and French governments placed the territories under the United Nations Trusteeship. Ten years later British Togoland was incorporated into the Gold Coast, and French Togoland became an autonomous republic within the French Union.
Togo gained independence in 1960. The economy rests largely on agriculture, although the country's phosphate reserves are also significant. Savanna- type vegetation is predominant in Togo. On the southern plateaus large trees, including the baobab, are common but sparse in the north. The southwestern highlands are covered with tropical forest- also found the river valleys. The coastal zone is dotted with mangroves and reed swamps.
The population of Togo is made up of 30 ethnic groups, many of whom are immigrants from other parts of Western Africa. The groups indigenous to Toga live in the north and southwest. Other ethnic groups include: Gur speaking peoples, The Gurma: The Natimba, the Kebu, the Kwa, the Adels, and the Ahola.
Almost half of Togolese are Catholics, with 13.7% Islam, 9.9% Independent and other Christian, 9.5% Protestant, 4.9% Traditional and 1.2% non religious.
Mining and quarrying are dominant economic activities in Togo with iron ore, bauxite, uranium and other minerals adding support to the economy.
Togo's GDP stands at 8.13 billion USD.
Until 1884 what is now Togo was an intermediate zone between the states of Asante and Dahomey, and its various ethnic groups lived in general isolation from each other. In 1884 it became part of Togoland German protectorate, which was later occupied by British and French forces in 1914. In 1922 The League of Nations assigned Togoland to France and the western portion to Britain. In 1946 the British and French governments placed the territories under the United Nations Trusteeship. Ten years later British Togoland was incorporated into the Gold Coast, and French Togoland became an autonomous republic within the French Union.
Togo gained independence in 1960. The economy rests largely on agriculture, although the country's phosphate reserves are also significant. Savanna- type vegetation is predominant in Togo. On the southern plateaus large trees, including the baobab, are common but sparse in the north. The southwestern highlands are covered with tropical forest- also found the river valleys. The coastal zone is dotted with mangroves and reed swamps.
The population of Togo is made up of 30 ethnic groups, many of whom are immigrants from other parts of Western Africa. The groups indigenous to Toga live in the north and southwest. Other ethnic groups include: Gur speaking peoples, The Gurma: The Natimba, the Kebu, the Kwa, the Adels, and the Ahola.
Almost half of Togolese are Catholics, with 13.7% Islam, 9.9% Independent and other Christian, 9.5% Protestant, 4.9% Traditional and 1.2% non religious.
Mining and quarrying are dominant economic activities in Togo with iron ore, bauxite, uranium and other minerals adding support to the economy.
Togo's GDP stands at 8.13 billion USD.